Salesforce now allows you to control whether Apex runs database operations in user mode or system mode. With the new AccessLevel parameter in Database methods, you can enforce user-mode access, ensuring that field-level security (FLS), sharing rules, and CRUD permissions of the running user are respected.
By default, Apex executes in system mode, where security permissions are bypassed. However, with this enhancement, you can invoke Apex in user mode, improving security and ensuring that database operations align with user permissions.
This update provides greater flexibility and enhances security by ensuring that Apex operations comply with Salesforce’s permission model.

By default, Apex runs in System Mode, where it bypasses all CRUD, field-level security (FLS), and sharing rules. This means the code executes with full access to all objects and fields, regardless of the running user’s permissions. System Mode is commonly used in triggers, batch jobs, scheduled Apex, and web services where unrestricted access is required. For example, when an Apex trigger updates a record, it can modify fields that the user normally wouldn’t have permission to edit.
With the introduction of User Mode, developers can now enforce security by specifying the AccessLevel.USER_MODE parameter in database operations. When Apex runs in User Mode, it respects the CRUD permissions, FLS, and sharing rules of the running user. This prevents unauthorized users from modifying or accessing restricted data, making it ideal for LWC controllers, Aura controllers, and API integrations that should align with user permissions.
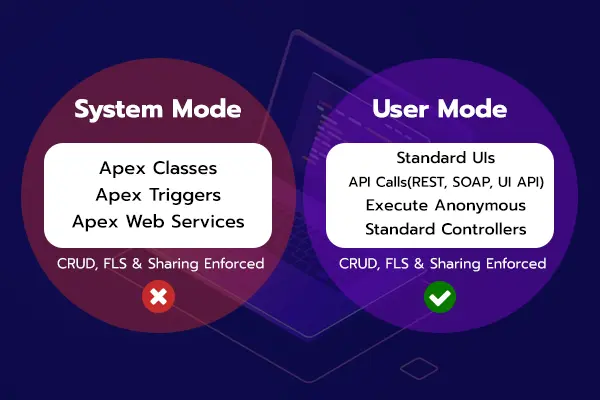
By leveraging User Mode, developers can build more secure applications while maintaining System Mode for scenarios that require elevated access. This enhancement ensures that Apex operations adhere to Salesforce’s security model, reducing the risk of unintended data exposure.
1. Enforcing Field-Level Security (FLS) using Security.stripInaccessible()
Before inserting, updating, or reading records, use Security.stripInaccessible() to remove restricted fields.
public void createAccount(Account acc) {
// Strip fields the user doesn’t have access to
SObject sanitizedAcc = Security.stripInaccessible(AccessType.CREATEABLE, acc).getRecords()[0];
// Insert the sanitized record
insert sanitizedAcc;
}
2. Enforcing User Mode in Database Operations
Salesforce introduced WITH USER_MODE to ensure that database operations respect user security settings.
public void insertAccount(Account acc) {
Database.SaveResult result = Database.insert(acc, AccessLevel.User_Mode);
if (!result.isSuccess()) {
System.debug('Insert failed: ' + result.getErrors()[0].getMessage());
}
}
3. Querying Data Securely with WITH USER_MODE
You can use SOQL with User Mode to respect sharing rules, CRUD, and FLS. Earlier the code without USER_MODE looked like:
if (Schema.SObjectType.Account.isAccessible() &&
Schema.SObjectType.Account.fields.Name.isAccessible() &&
Schema.SObjectType.Account.fields.OwnerId.isAccessible() &&
Schema.SObjectType.Account.fields.Support__c.isAccessible() &&
Schema.SObjectType.Account.fields.OwnerId.getReferenceTo()[0].getDescribe().isAccessible()) {
return [SELECT Name, Owner.Name FROM Account WHERE Support__C = 'Premier'];
} else {
throw new AuraHandledException('Access Denied');
}
Now we have a better way to handle it using USER_MODE.
return [SELECT Name, Owner.Name FROM Account WHERE Support__C = 'Premier' WITH USER_MODE];
4. Database operations can specify user or system mode.
Let's take an example of inserting a new account in user mode.
insert as user new Account(Name = 'VPC');
Account a = [SELECT Id, Name FROM Account WHERE Support__c = 'FREE TRAINING' WITH USER_MODE];
a.Rating = 'Hot';
update as system a;
Now we have a better way to handle it using USER_MODE.
return [SELECT Name, Owner.Name FROM Account WHERE Support__C = 'Premier' WITH USER_MODE];
5. New AccessLevel Class in Apex
Salesforce introduced the AccessLevel class to explicitly define whether Apex database operations should run in User Mode or System Mode. This class provides a cleaner, more consistent way to control execution behavior for CRUD, Field-Level Security (FLS), and Sharing Rules.
Example of Database DML methods
Database.insert( new Account(Name = 'VPC'),
AccessLevel.USER_MODE
);
Account a = Database.query('SELECT Id, Name FROM Account WHERE Rating = \'Hot\'',
AccessLevel.USER_MODE
);
Handling Field-Level Security (FLS) Errors in Apex
When using AccessLevel.USER_MODE, Salesforce automatically enforces CRUD and Field-Level Security (FLS). If a user tries to access a restricted field, an error will occur. Here's how to handle these errors gracefully.
List srList = Database.insert(
new SObject[] {
new Account(Name='VPC', AnnualRevenue=1), // no FLS edit on AnnualRevenue
new Contact(LastName='Singh', Email='vpc1'), // no FLS view on Email
},
false, // allOrNone
AccessLevel.USER_MODE
);
System.assert(!srList.get(0).getErrors()[0].getFields().contains('AnnualRevenue’),
'Missing Account.AnnualRevenue FLS');
System.assert(!srList.get(1).getErrors()[0].getFields().contains('Email’),
'Missing Contact.Email FLS')
String searchquery = 'Find \'VPC\' IN ALL FIELDS RETURNING Account(id,name)';
List> searchList = Search.query(searchquery, AccessLevel.USER_MODE);
Search.SearchResults sr = Search.find(searchquery, AccessLevel.USER_MODE);
Search.SuggestionResults sgr = Search.suggest('all', 'Account', null,
AccessLevel.USER_MODE);
List> searchList = [FIND 'website123' RETURNING Account(id,name)
with user_mode];
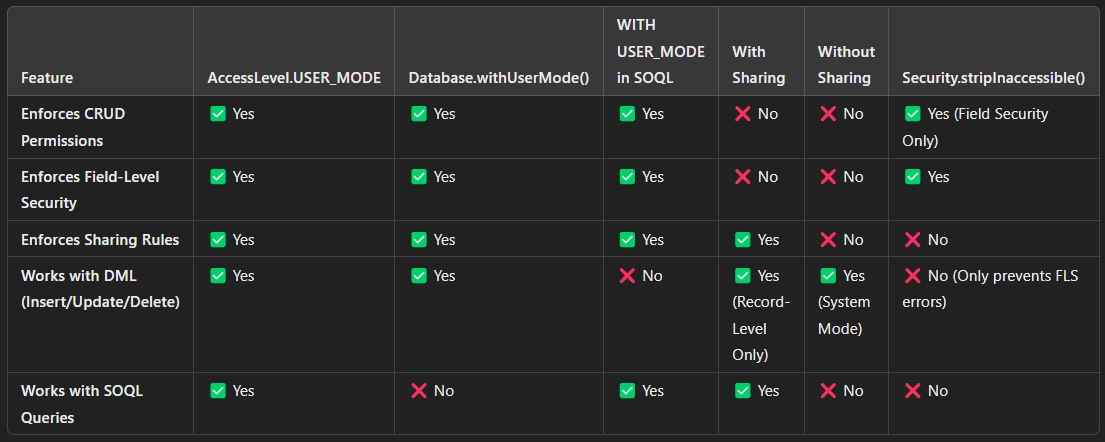
There are several methods for developers to secure their apex code depending upon the use case. However, USER_MODE ensures that Apex enforces security settings consistently across SOQL queries and DML operations (Insert, Update, Delete). Let's take a look at below table that compares traditional methods like With Sharing, Without Sharing, and Security.stripInaccessible(), highlighting their strengths and limitations.
If you need expert guidance on Apex security, Salesforce development, or optimizing your org’s security model, Consult our team of experienced Salesforce consultants is here to help. Whether it's implementing USER_MODE, enforcing CRUD/FLS, or building scalable solutions, we provide tailored support to meet your business needs. Contact us today to ensure your Salesforce implementation is secure, efficient, and future-proof!
Fill out the following form & we will get back to you.